Horns
Horn shape
H / h / h+
A Veilhorn can only have 1-2 horns, which must be located on their head. The exception is if the Polycerate mutation is present.
The horn shape is determined by the H/h/h+ gene, with the following possible combinations:
HH (straight)
Hh (straight)
hh (curved)
Hh+ (curved)
hh+ (coiled)
h+h+ (coiled)
Straight
HH / Hh
Straight horns should always be either completely straight, or have a very subtle curve to them, as shown on the examples below.
Smooth straight
HH / Hh
+
aa / ab / bb
Twirled straight
HH / Hh
+
Aa / Ab
Ridged straight
HH / Hh
+
Ba / Bb
Spined straight
HH / Hh
+
AA / AB / BB
Curved
hh / Hh+
Curved horns should have 1-2 curves, either forwards or backwards (or both), but may not coil around itself.

Smooth curved
hh / Hh+
+
aa / ab / bb

Twirled curved
hh / Hh+
+
Aa / Ab

Ridged curved
hh / Hh+
+
Ba / Bb
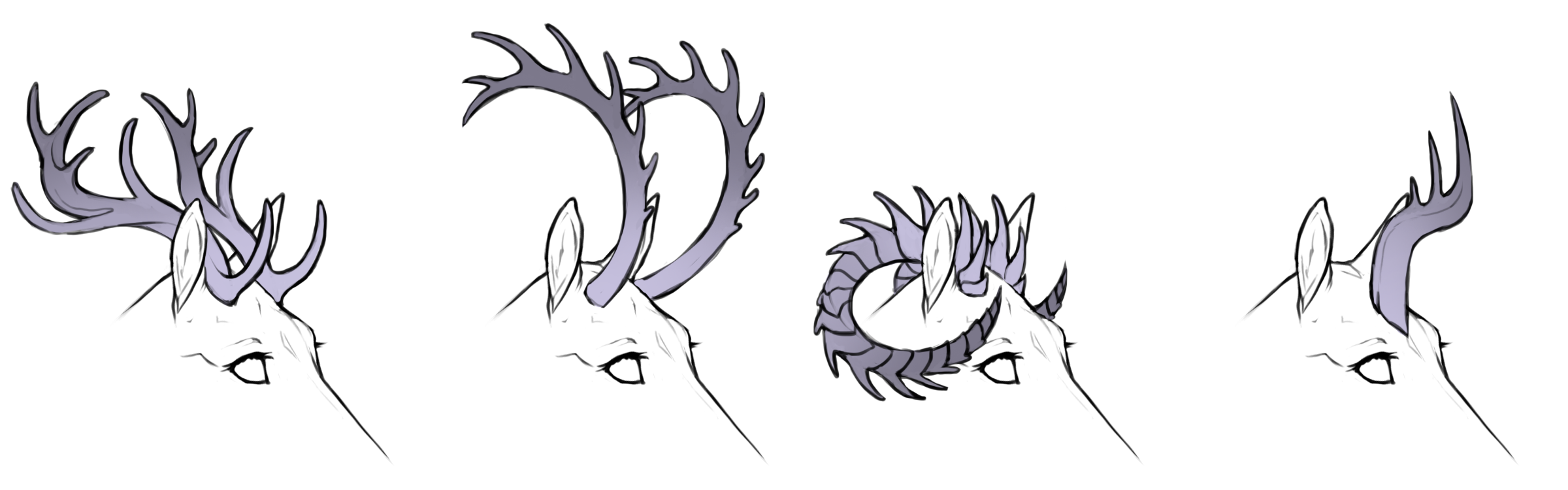

Spined curved
hh / Hh+
+
AA / AB / BB
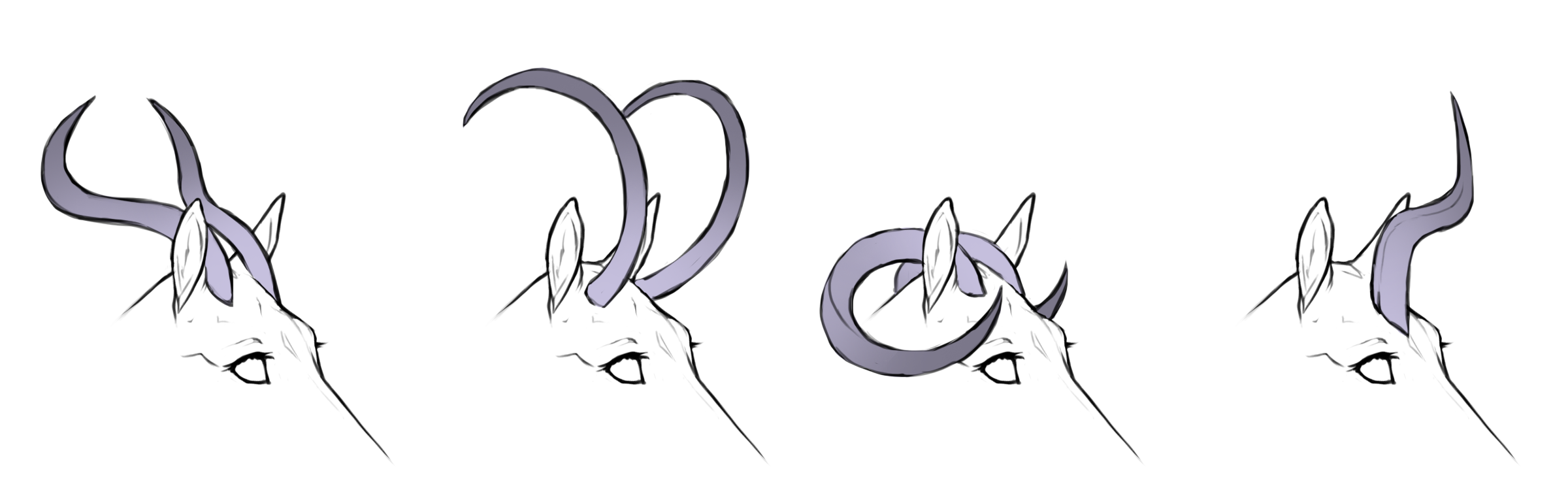
Coiled
hh+ / h+h+
Coiled horns causes the horns to be so curved that they coil around themselves into spirals.
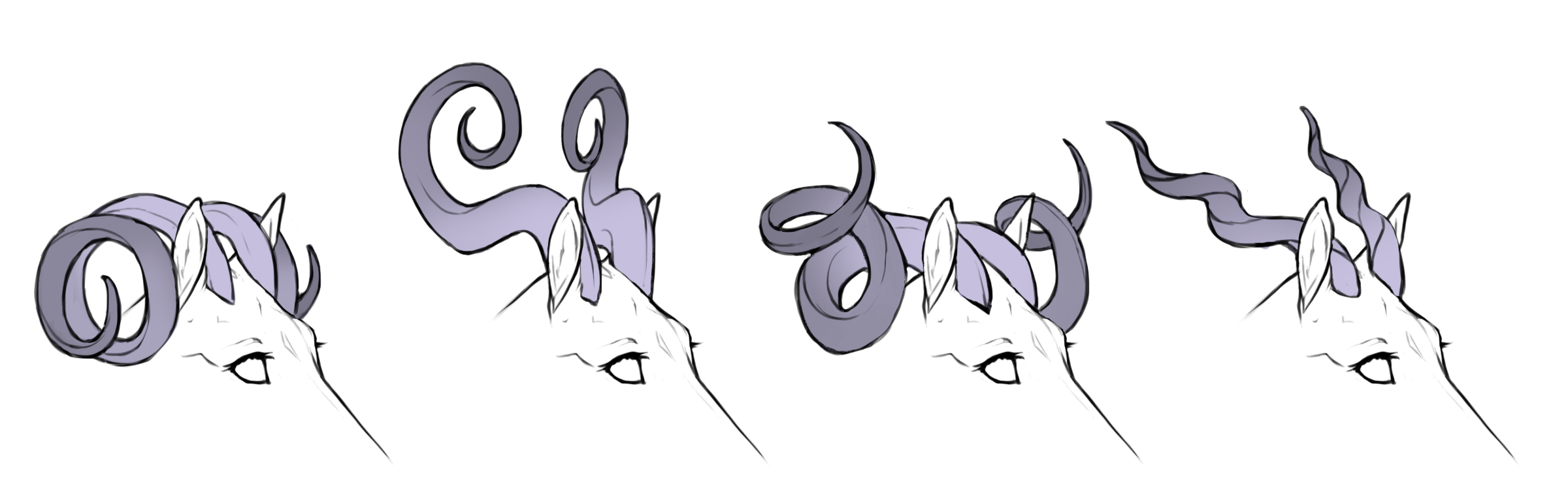
Smooth coiled
hh+ / h+h+
+
aa / ab / bb
Twirled coiled
hh+ / h+h+
+
Aa / Ab
Ridged coiled
hh+ / h+h+
+
Ba / Bb
Spined coiled
hh+ / h+h+
+
AA / AB / BB
Horn type
A / a / B / b
A Veilhorn can only have 1-2 horns, which must be located on their head. The exception is if the Polycerate mutation is present.
The horn type is determined by the A/a/B/b gene, with the following possible combinations:
aa (smooth)
ab (smooth)
bb (smooth)
Aa (twirled)
Ab (twirled)
Ba (ridged)
Bb (ridged)
AA (spined)
AB (spined)
BB (spined)
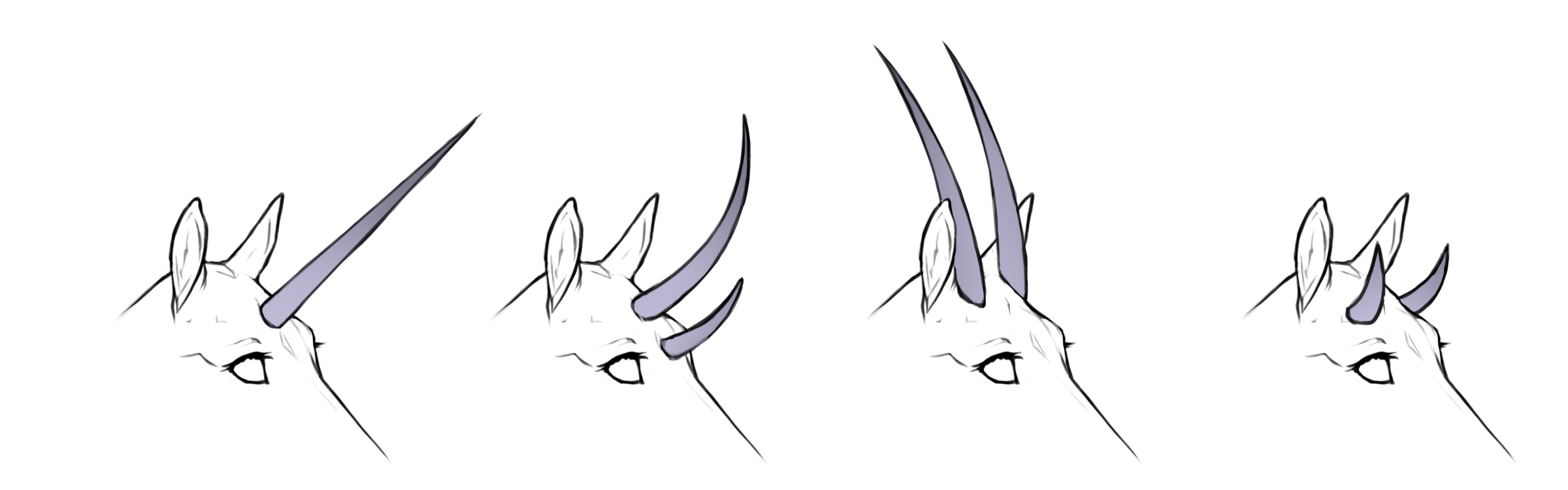
Smooth
aa / ab / bb
Smooth horns will always be completely smooth, with no extra points, ridges or textures.

Smooth straight
HH / Hh
+
aa / ab / bb

Smooth curved
hh / Hh+
+
aa / ab / bb

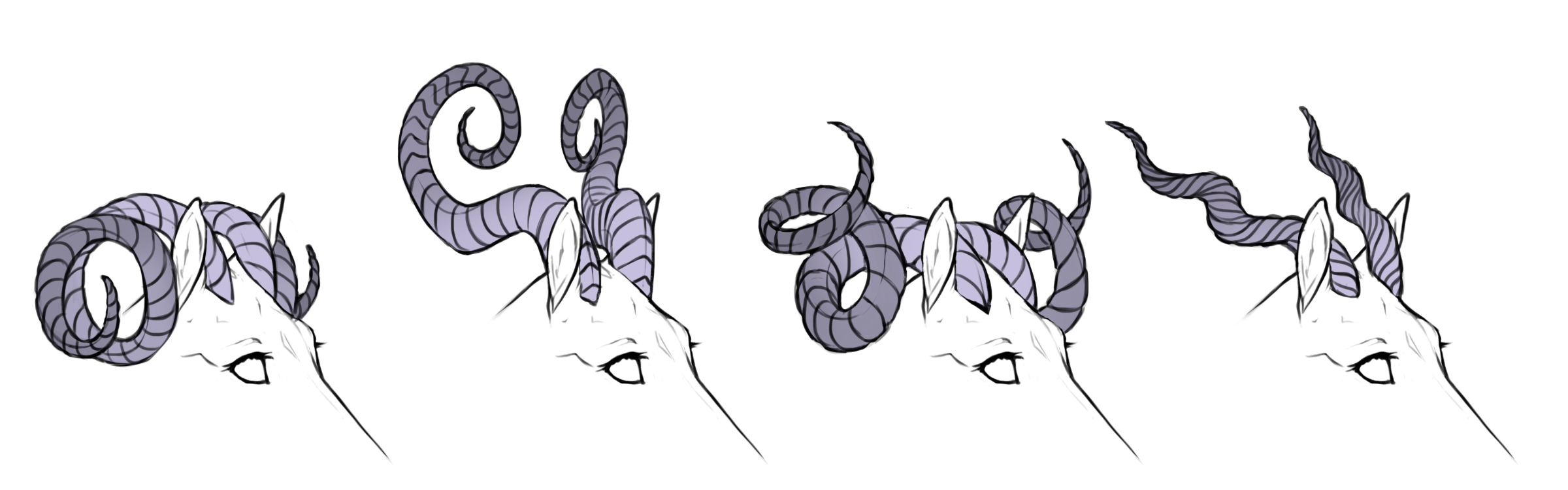
Smooth coiled
hh+ / h+h+
+
aa / ab / bb
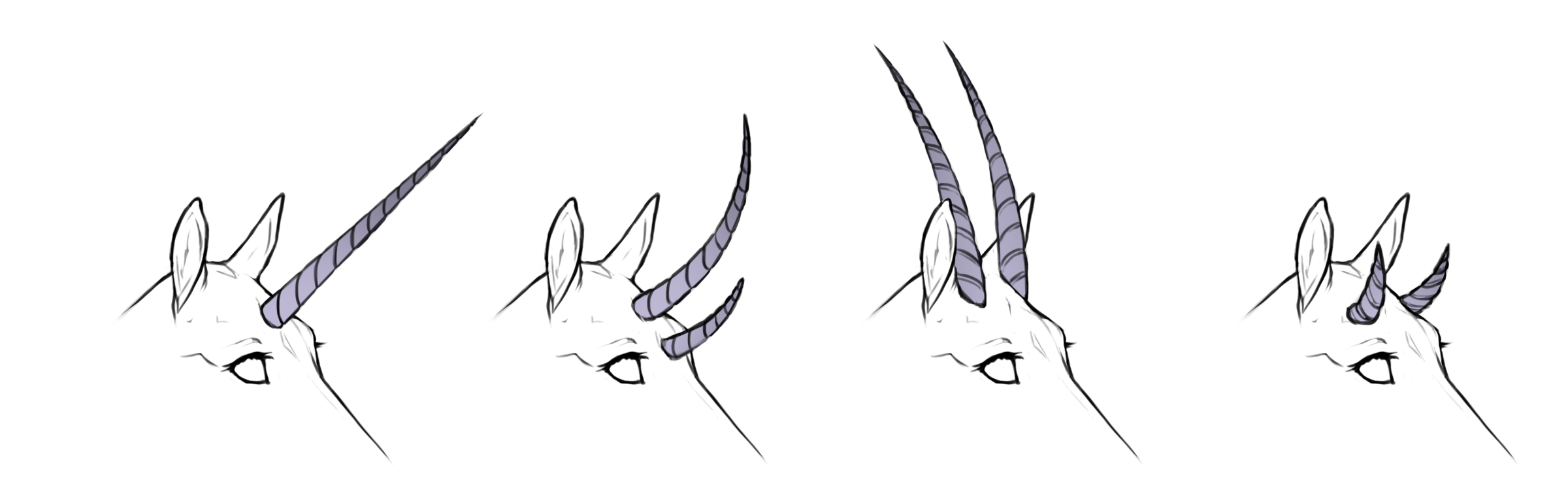
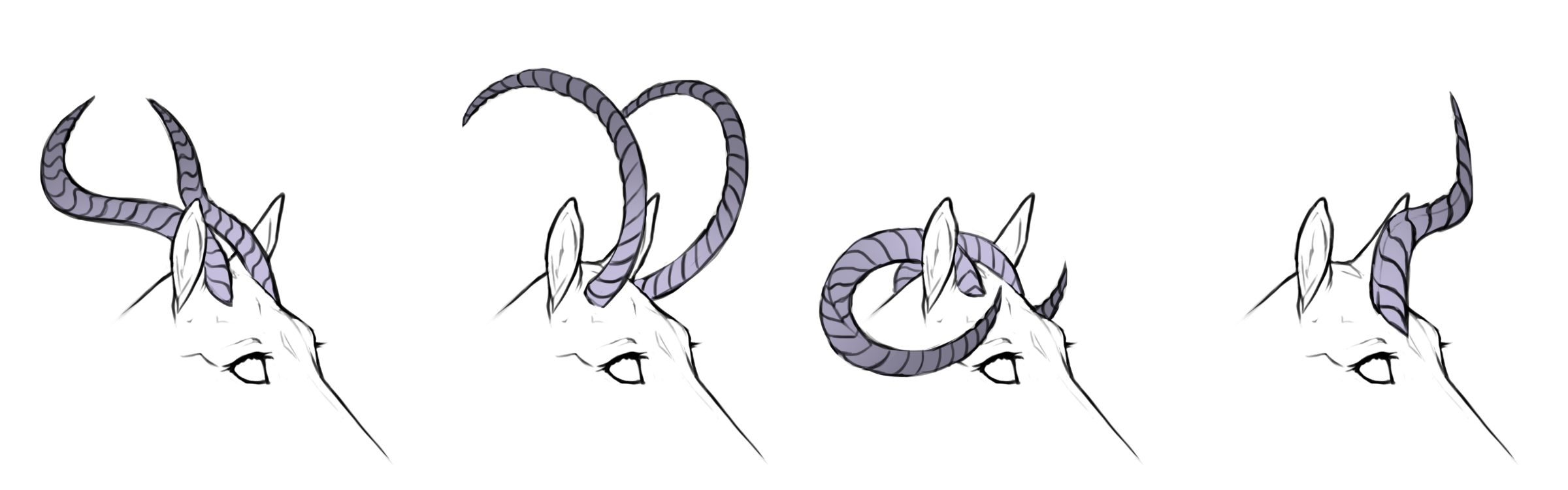
Twirled
Aa / Ab
Twirled horns will have the "spun" appearance of a traditional unicorn horn, like a spire seashell.

Twirled straight
HH / Hh
+
Aa / Ab

Twirled curved
hh / Hh+
+
Aa / Ab

Twirled coiled
hh+ / h+h+
+
Aa / Ab
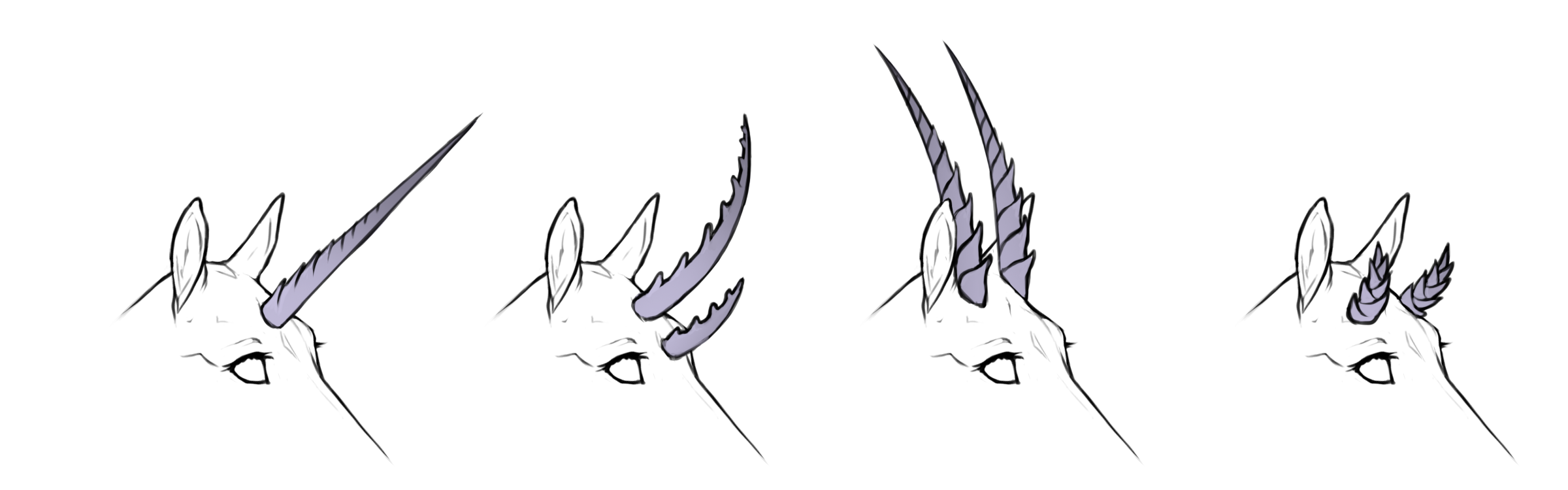
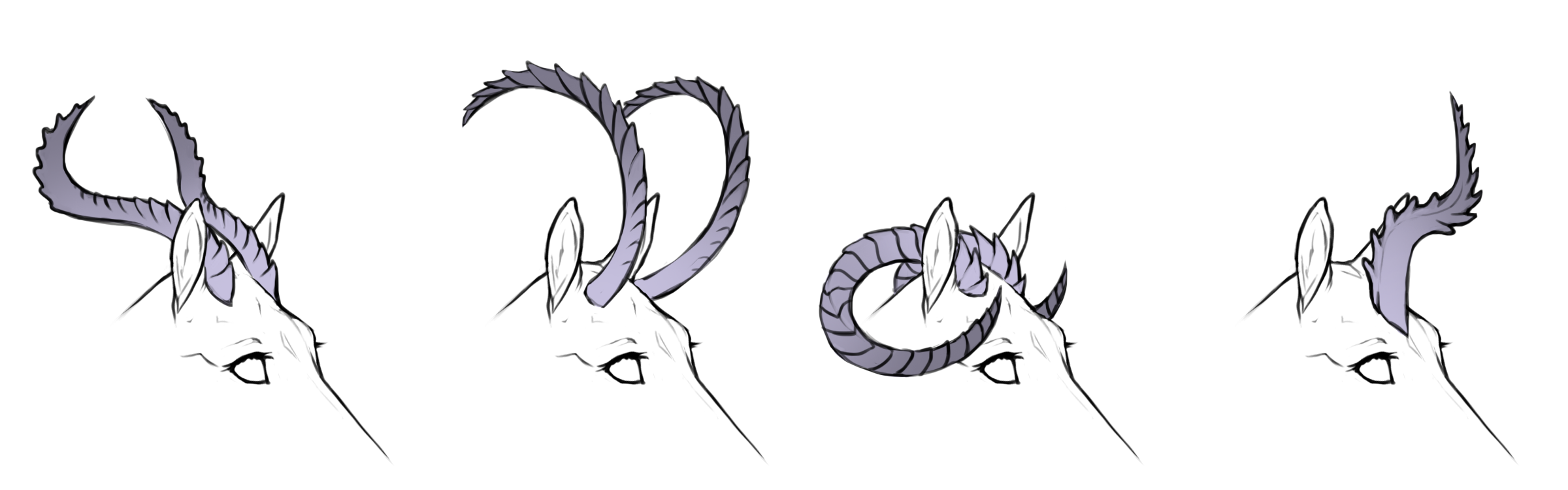
Ridged
Ba / Bb
Ridged horns are more textured, scale-like or with small spikes. Ridged horns can be partially smooth or twirled, but must have some ridged texture present. If spines/spikes are present they must not be too tall and may not be confused for spined horns.

Ridged straight
HH / Hh
+
Ba / Bb

Ridged curved
hh / Hh+
+
Ba / Bb

Ridged coiled
hh+ / h+h+
+
Ba / Bb
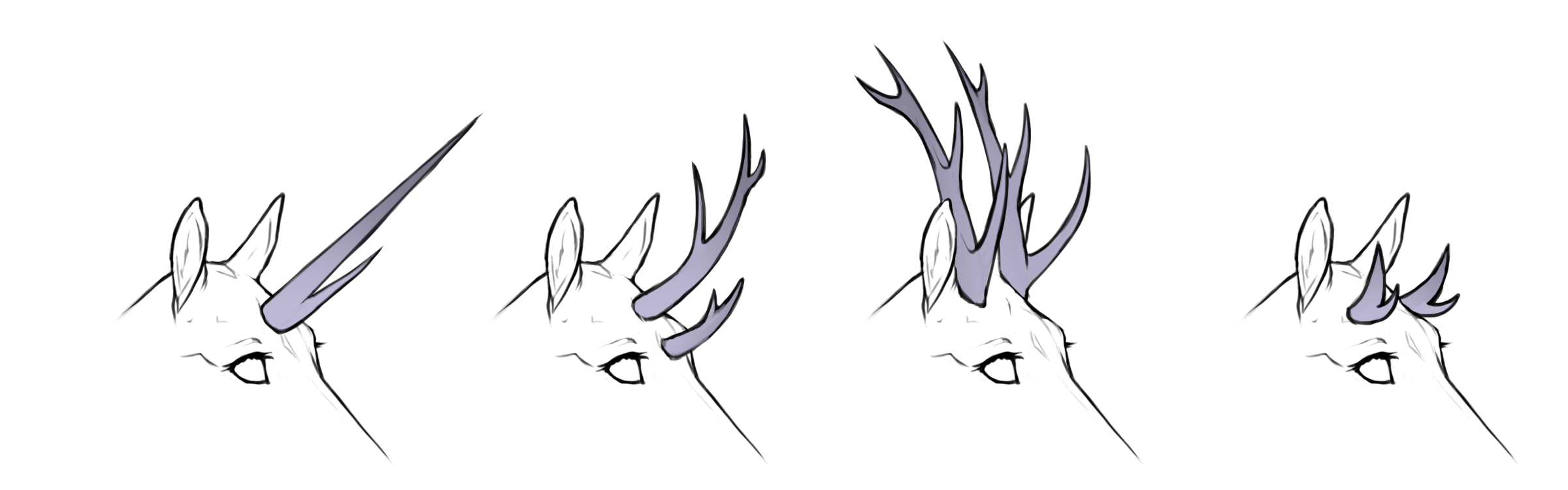
Spined
AA / AB / BB
Spined horns causes a typical antler-appearance with large spikes. Spined horns may optionally appear ridged/scaled as well, but must always have long spines visible.
Spined horns are allowed to be broad and palmate (flat) with spines along the edges similar to moose antlers.

Spined straight
HH / Hh
+
AA / AB / BB

Spined curved
hh / Hh+
+
AA / AB / BB

Spined coiled
hh+ / h+h+
+
AA / AB / BB
Appearance
Polycerate is a horn mutation causing the horse to have more than 2 horns.
The horns can grow on more locations than just the head, as long as the primary one or two horns are still located on the head.
Polycerate horns can have different shapes (for example straight and curved at the same time), but always have the same type (smooth/twirled/ridged/spined) - you can not have smooth straight and twirled straight at the same time, but you can have smooth straight and smooth coiled.
The primary 1-2 horns should still follow their shape listed in the horn genotype.
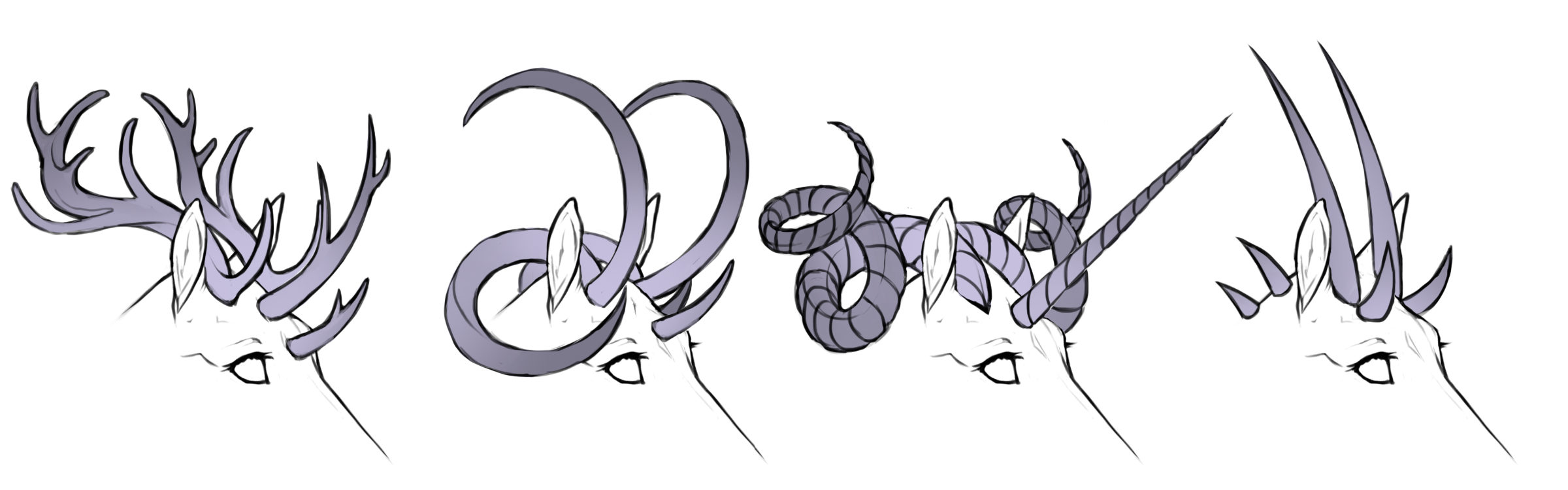
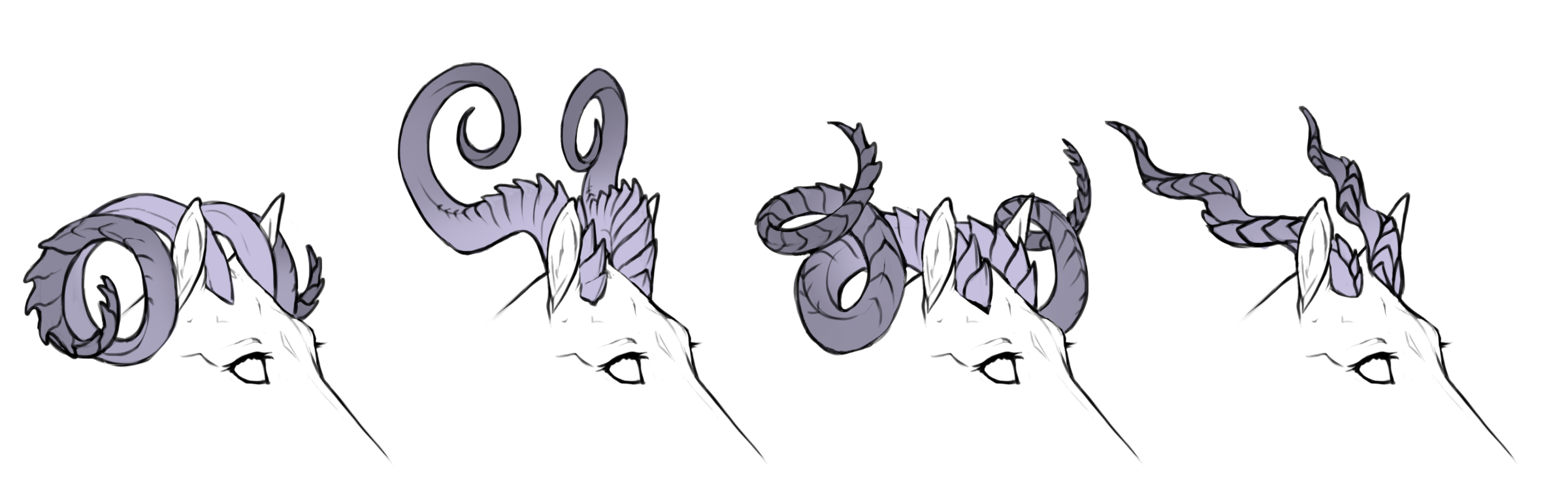
Various polycerate horns
From left to right: spined, smooth, twirled, smooth
Appearance
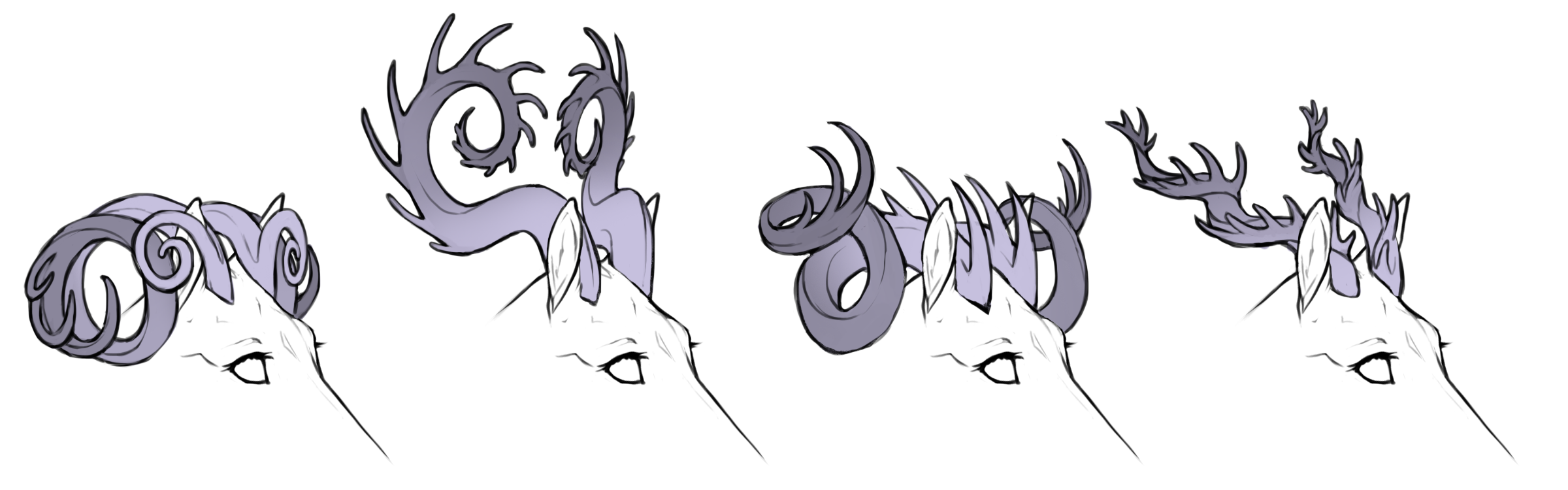
Webbed is a horn mutation causing the horns to grow or merge into itself or eachother, most notable on spined horns.
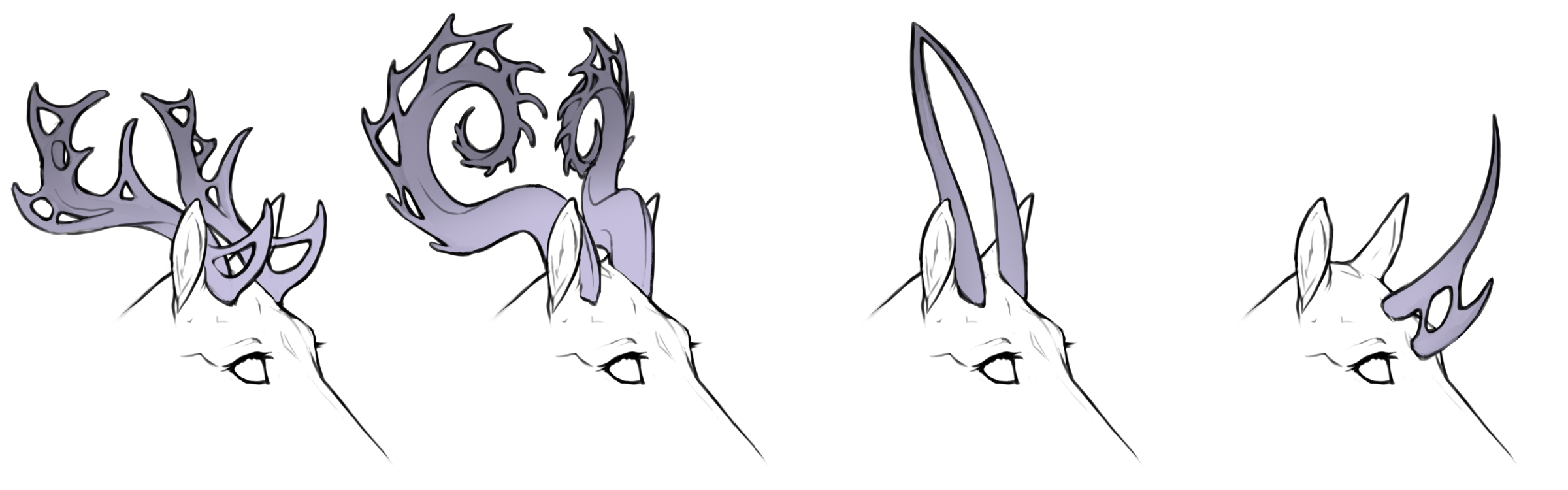

Various webbed horns
From left to right: spined curved, spined coiled, smooth straight, smooth straight