Genetic guide - Colors and markings
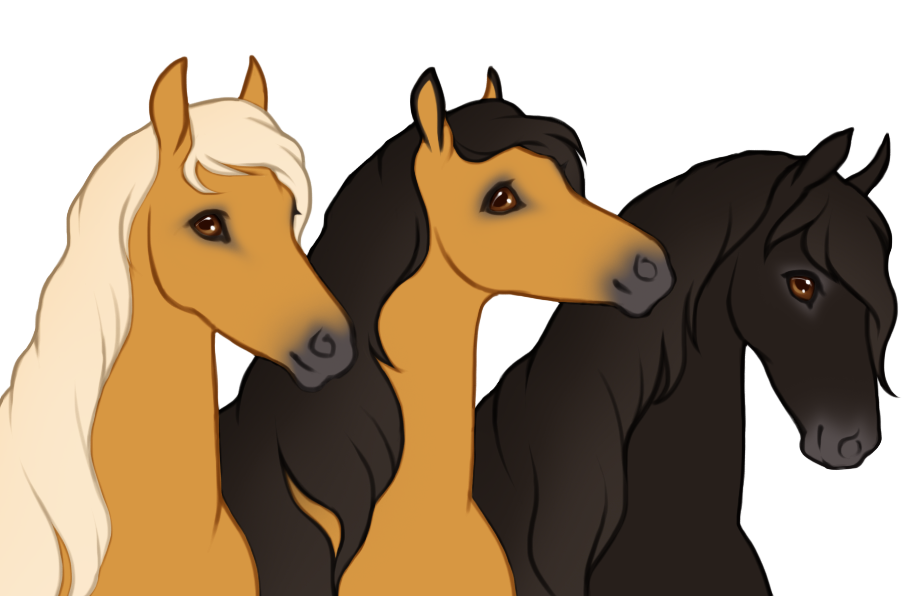
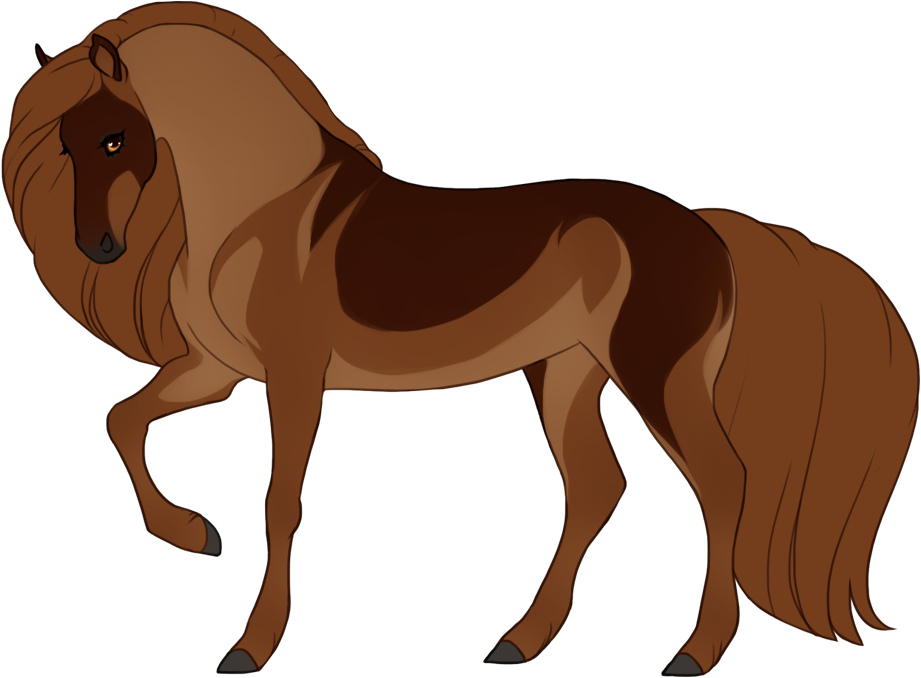
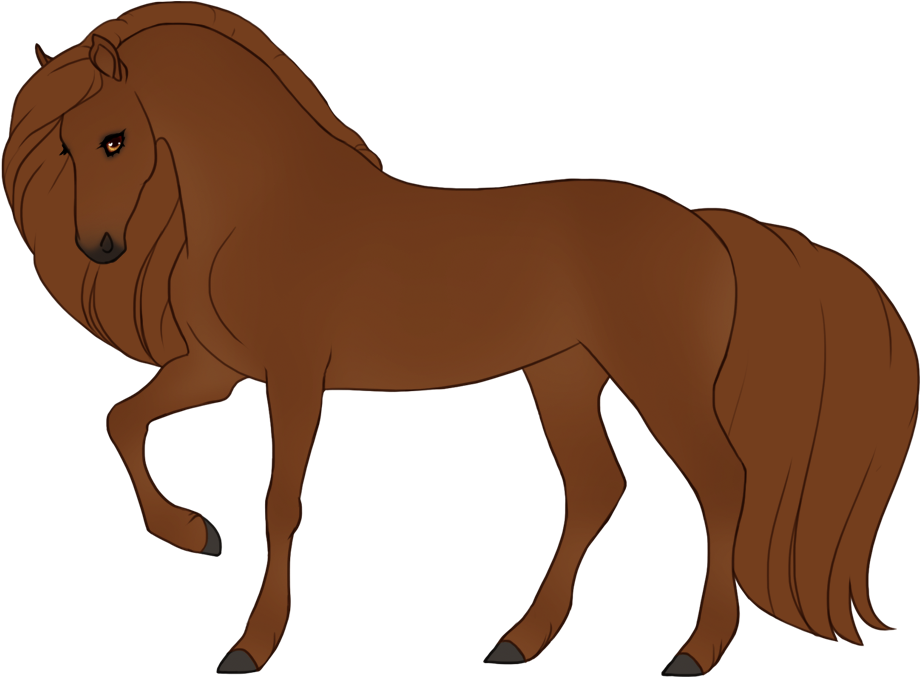
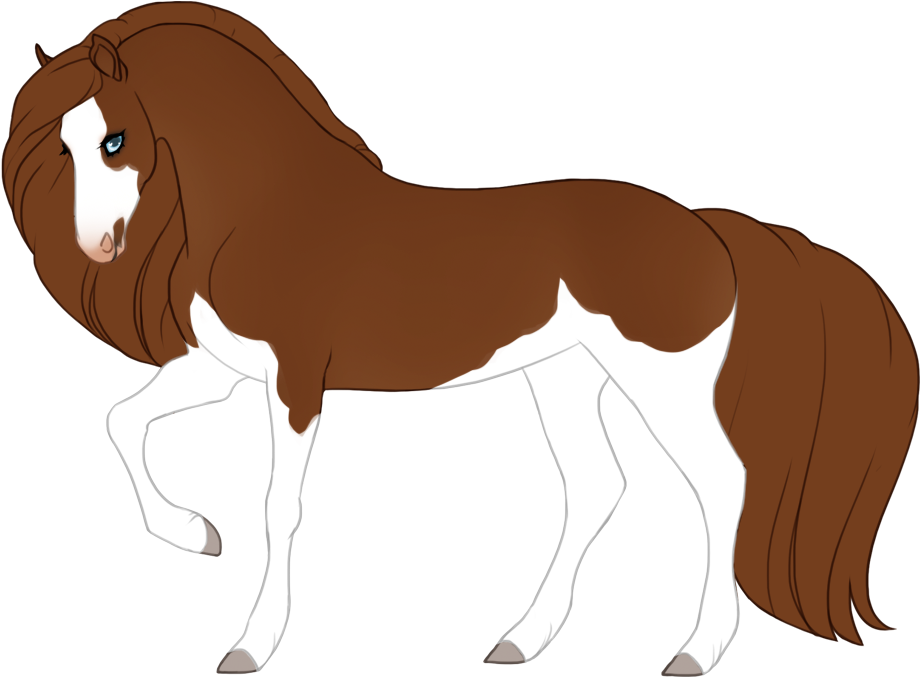
- Dilutions alter the base color of the horse as well as the mane and tail.
- Affects eye color unless otherwise specified (dun is the only dilution that doesn't affect eye color).
- Affects hoof and horn color unless otherwise specified (dun is the only dilution that doesn't affect hoof or horn color).
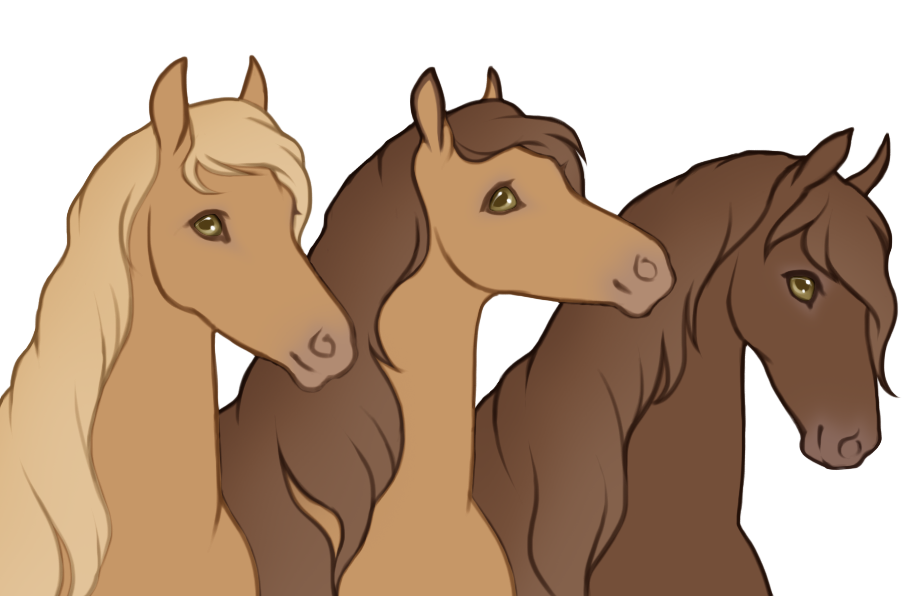
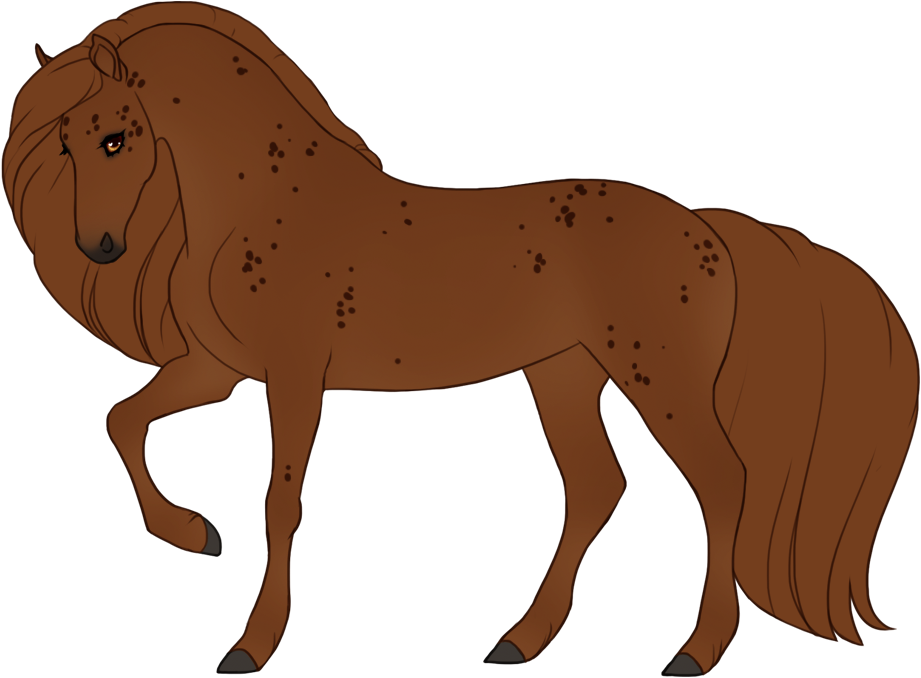
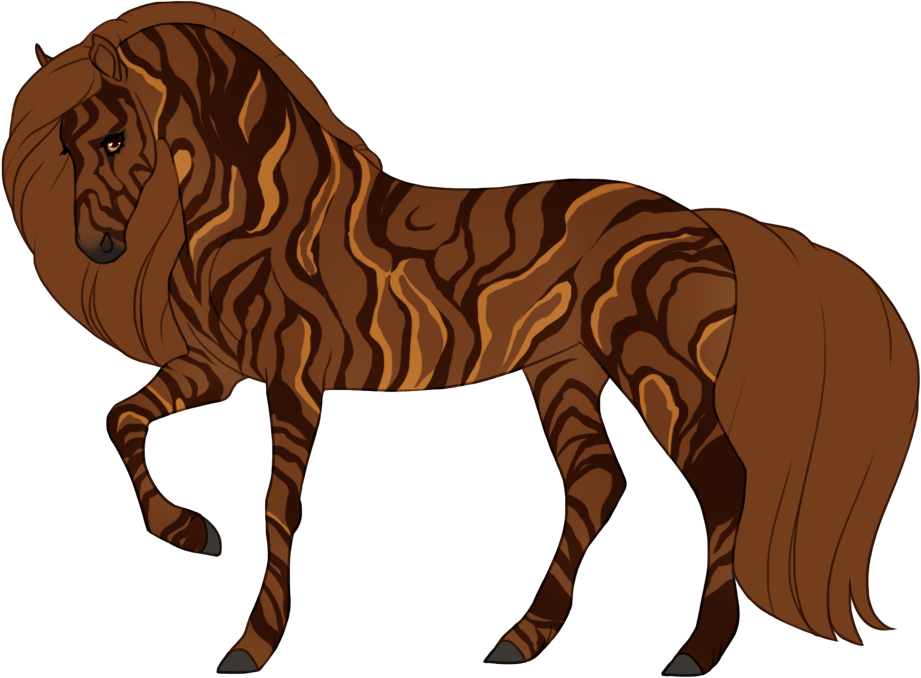
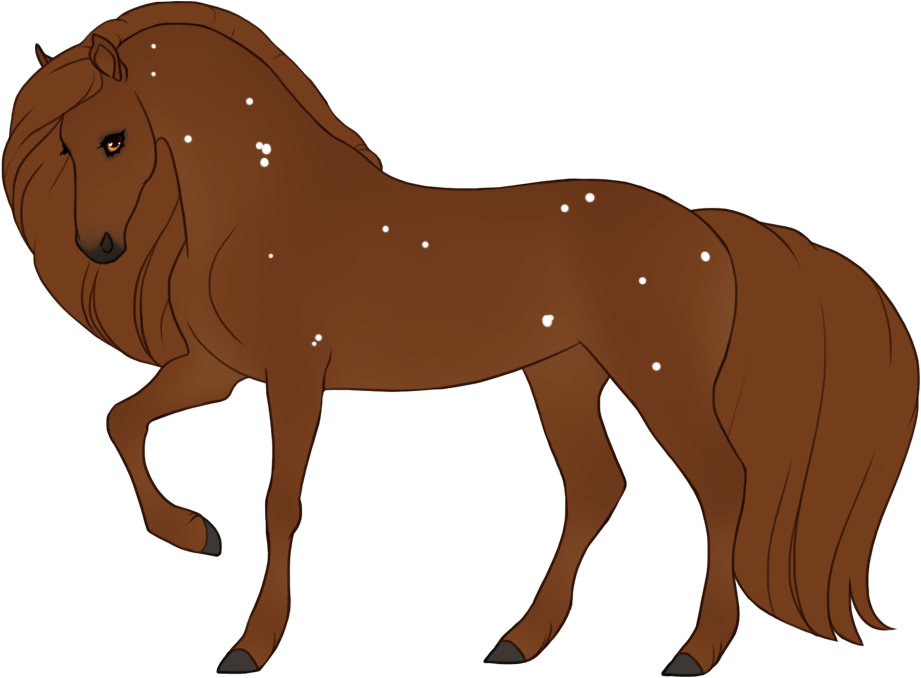
- Modifiers alter the appearance of the base color in different ways without diluting the color, which creates a wide variety of possible colors and patterns.
- Doesn't affect skin, eye or hoof/horn color. (Variegated affects mane/tail and hooves/horns the same way white patterns do)
- All modifiers always go below White patterns, except variegated which modifies white patterns itself.
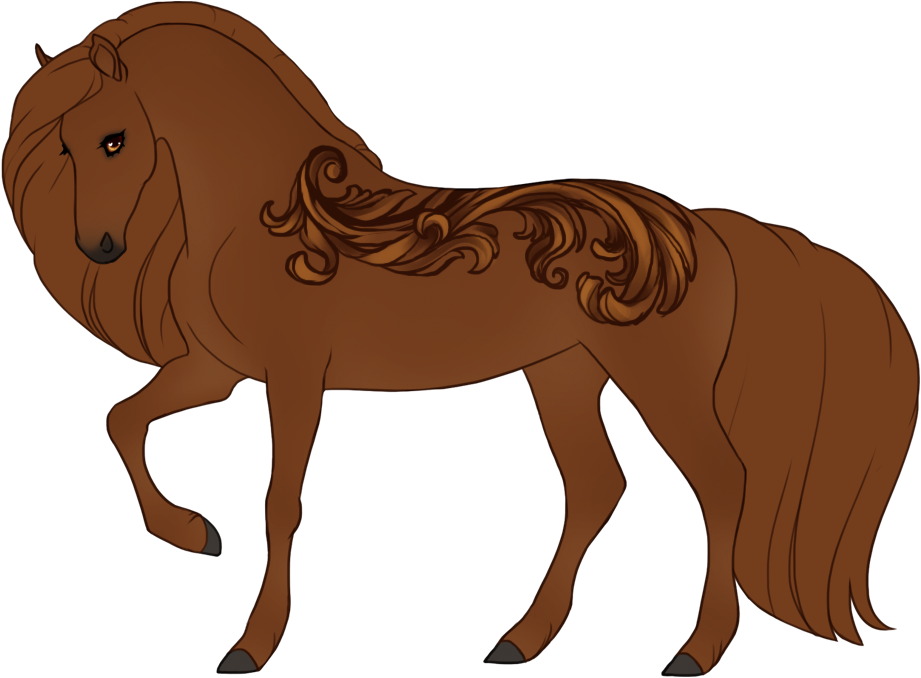
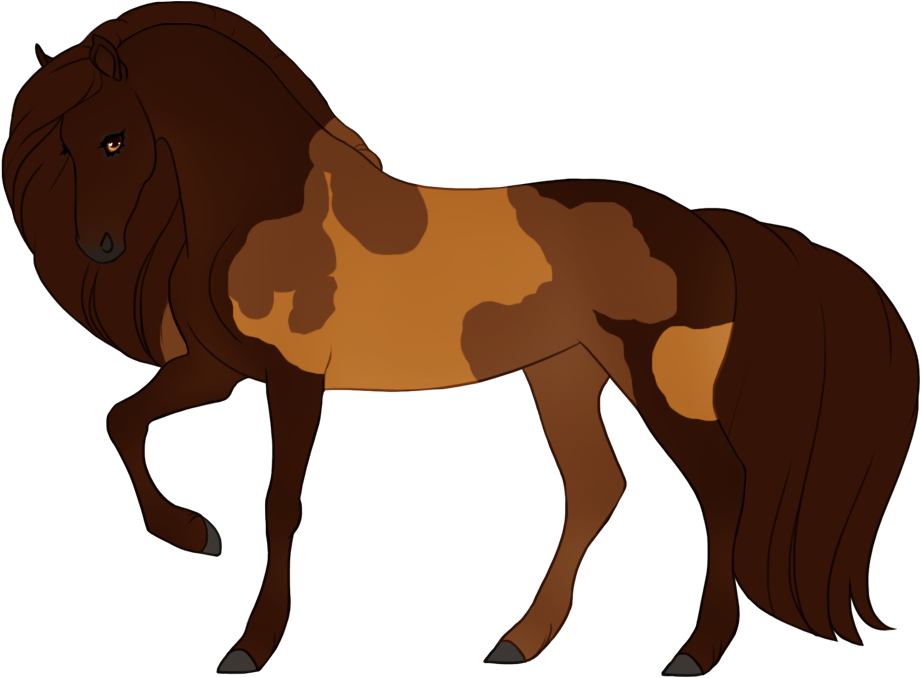
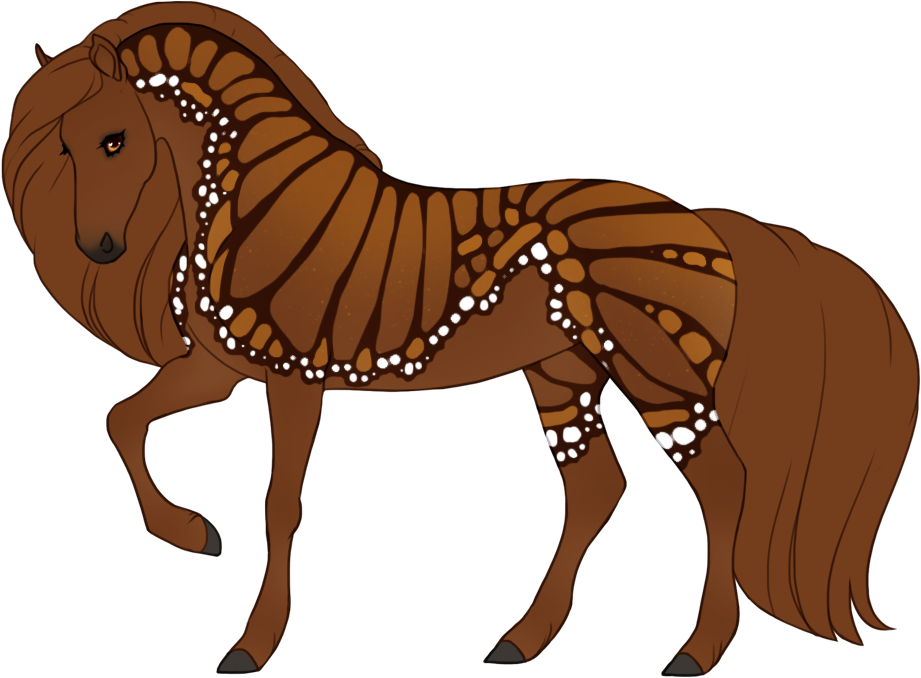
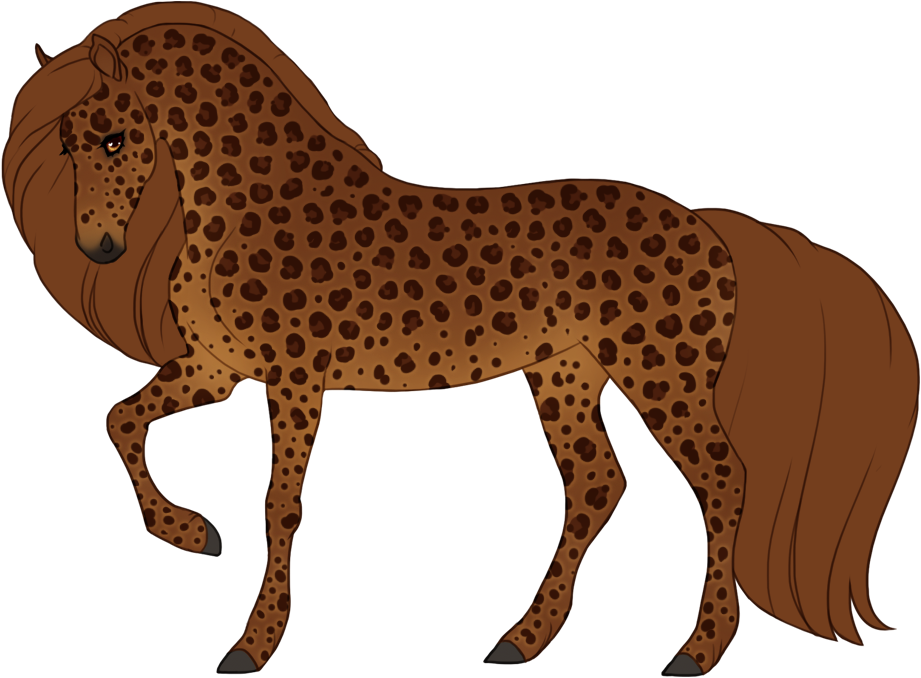
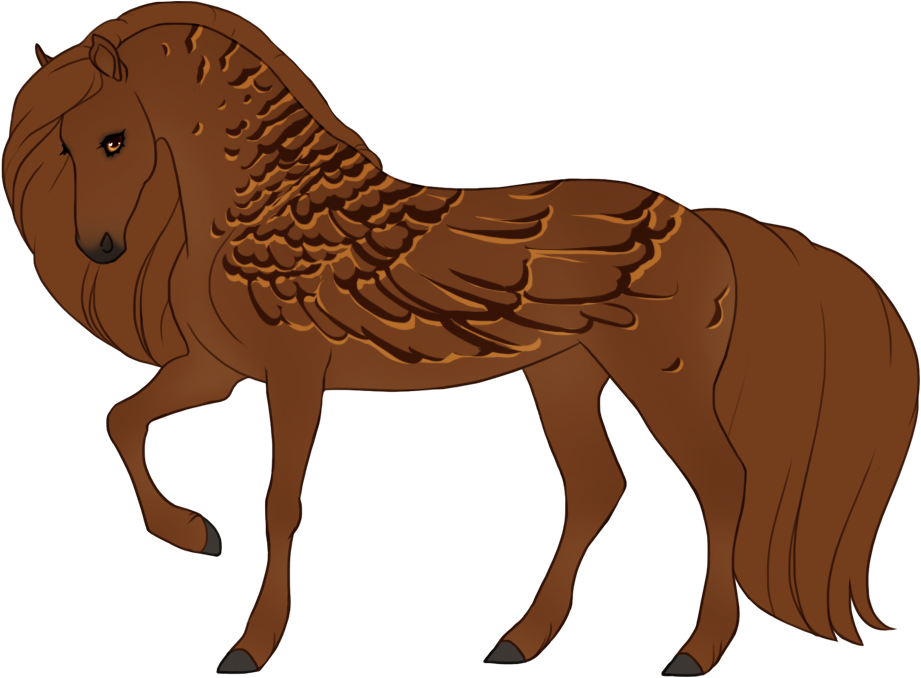
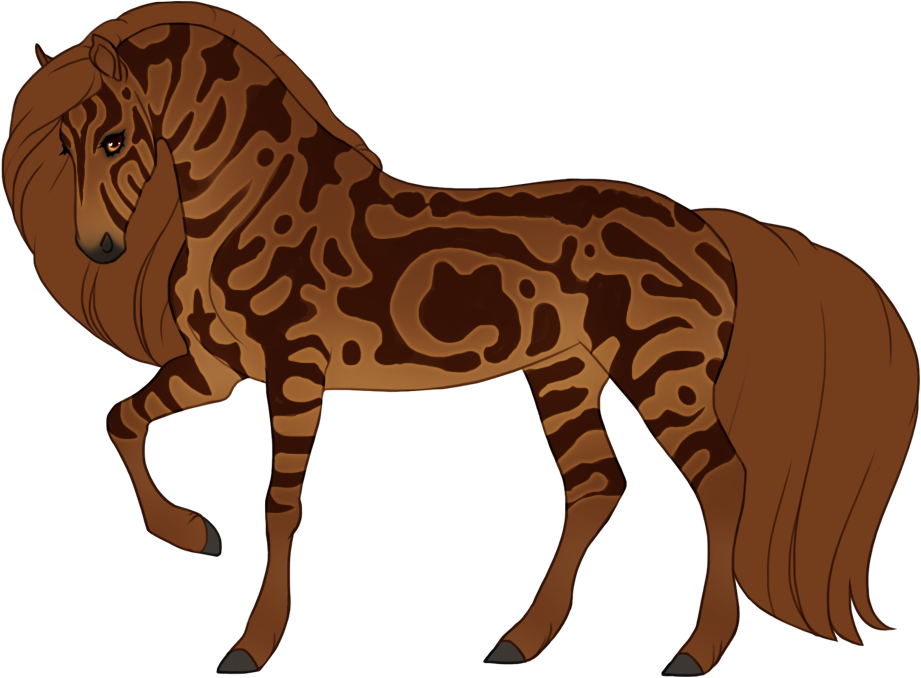
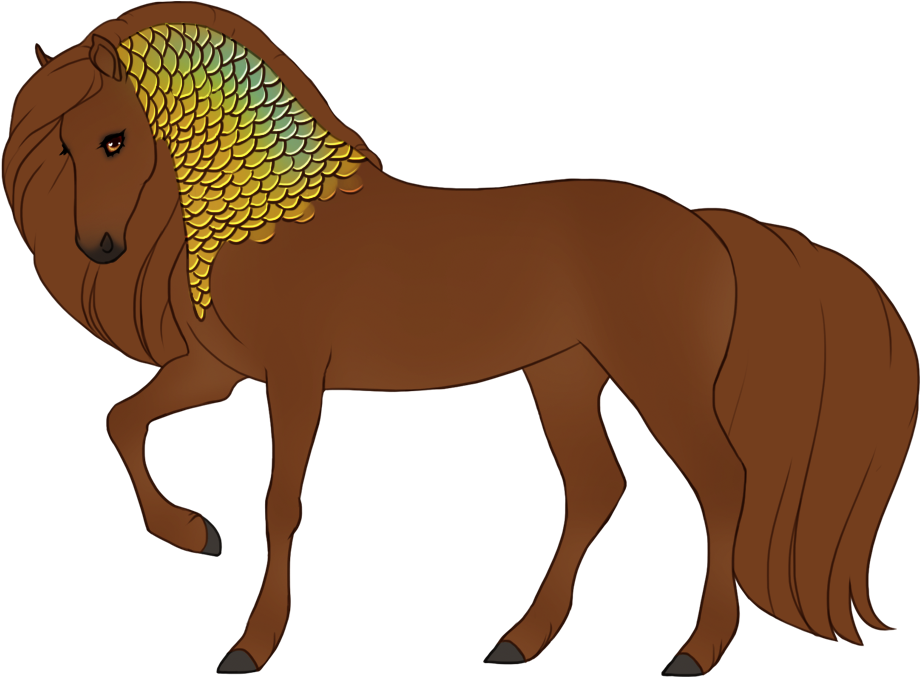
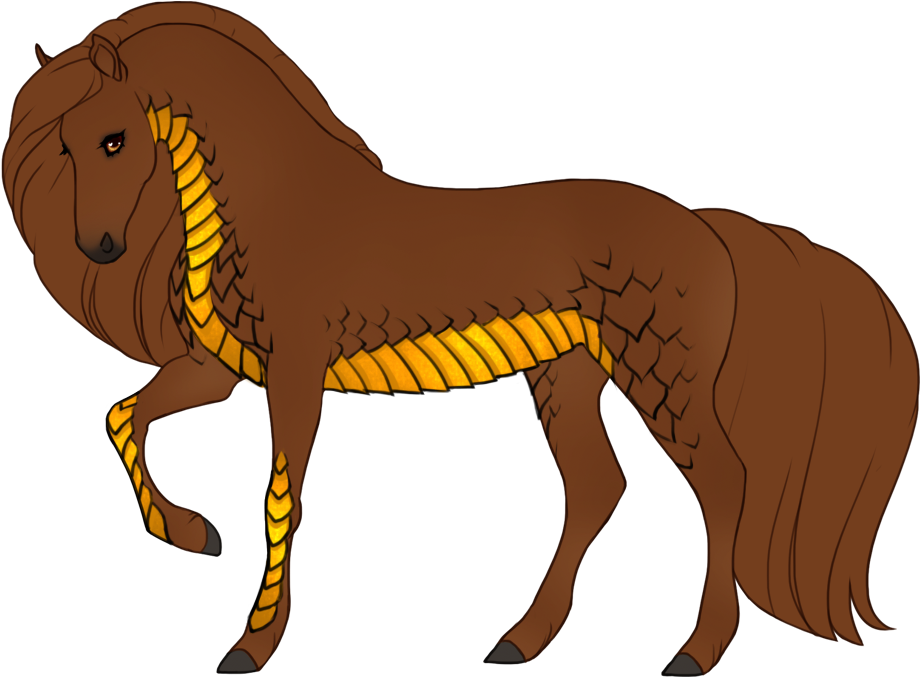
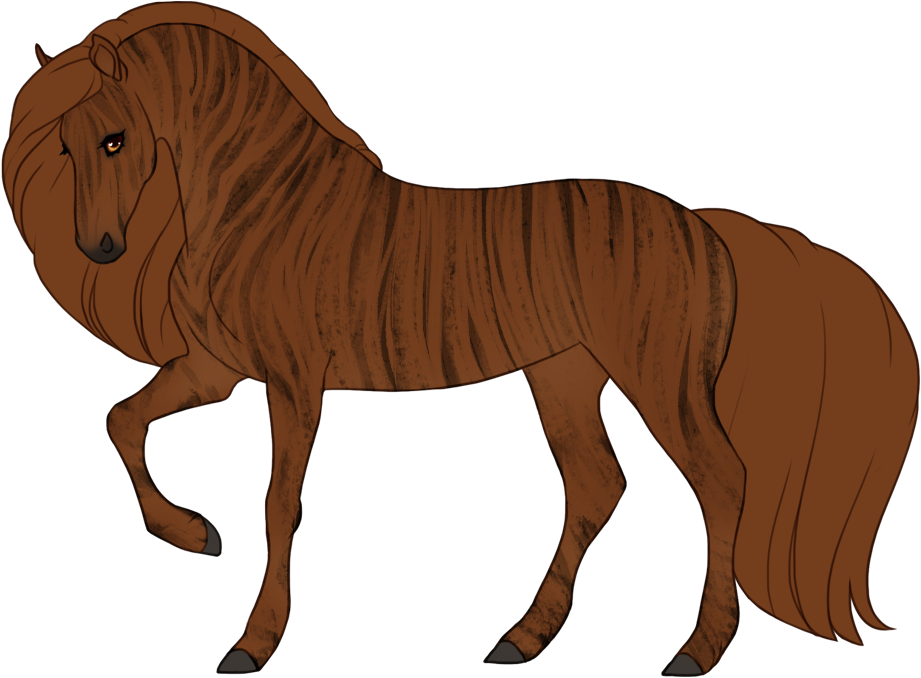
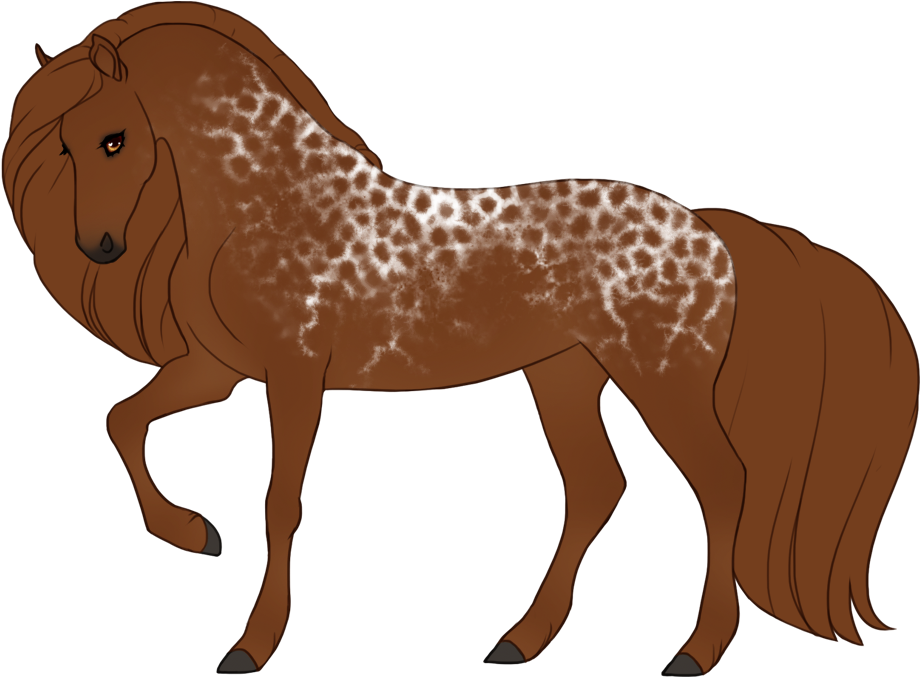
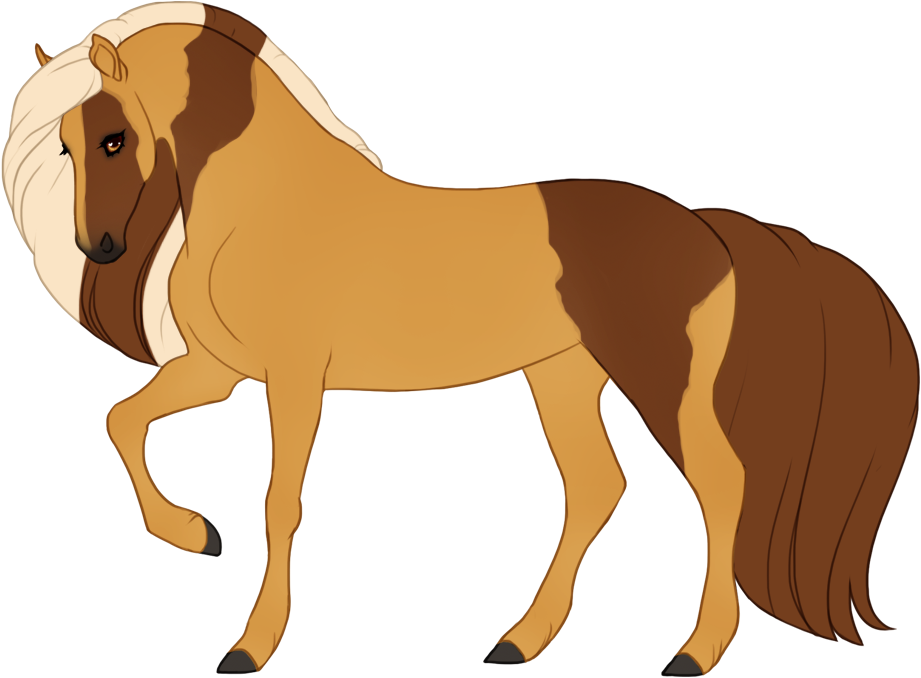
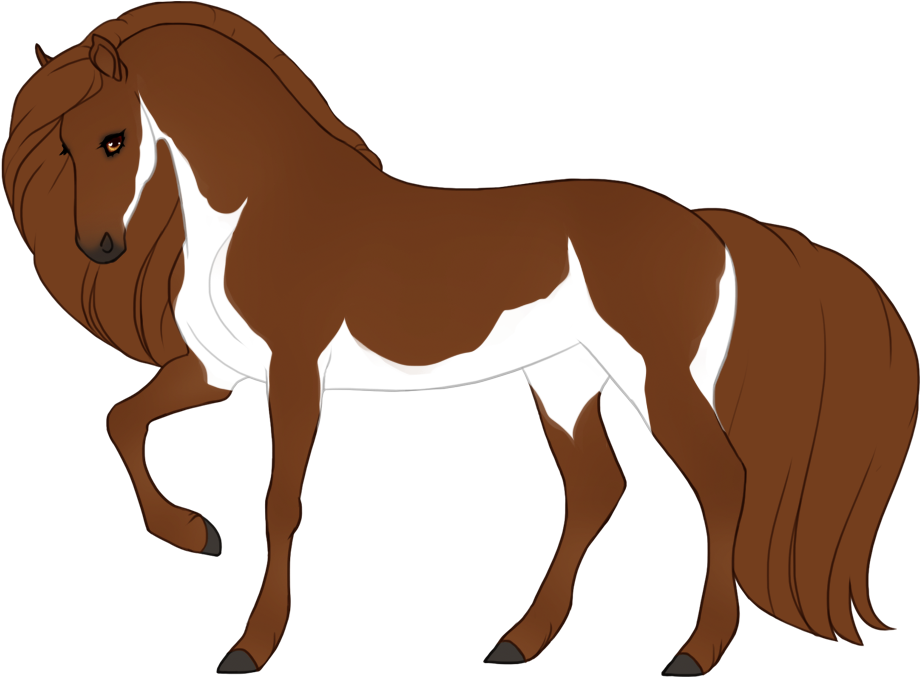
- Patterns are always darker than the base color, and can optionally have lighter accents.
- Can optionally be affected by certain Modifiers:
- Bronze turns patterns bronze or rich brown.
- Flaxen turns patterns creamy white or lighter than the base coat. (only affects chestnut-based (ee) coats)
- Silver turns patterns white or lighter than the base coat. (only affects black-based (EE or Ee) coats)
- Chromatic turns patterns into a different hue or saturation.
- Grey can leave the patterns unaffected (doesn't grey out), or leave the entire body unaffected and only the patterns grey out.
- Can be affected by Shimmer in many different ways, see shimmer guide for details.
- Can be affected by Primal, optionally turning the marking into the colour of the character's elemental alignment.
- Always goes below White patterns.
- Doesn't affect skin, eye or hoof/horn color.
- Can optionally affect mane/tail.
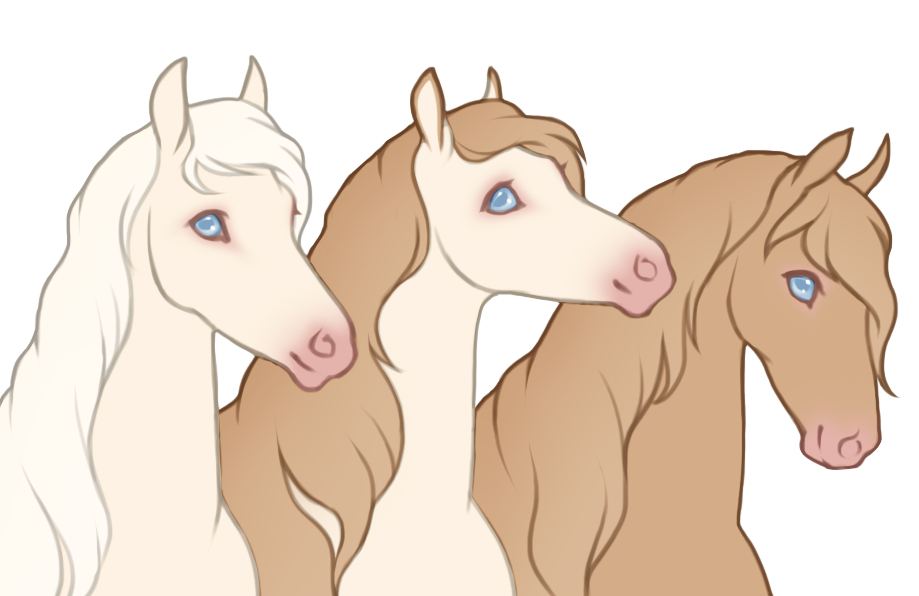
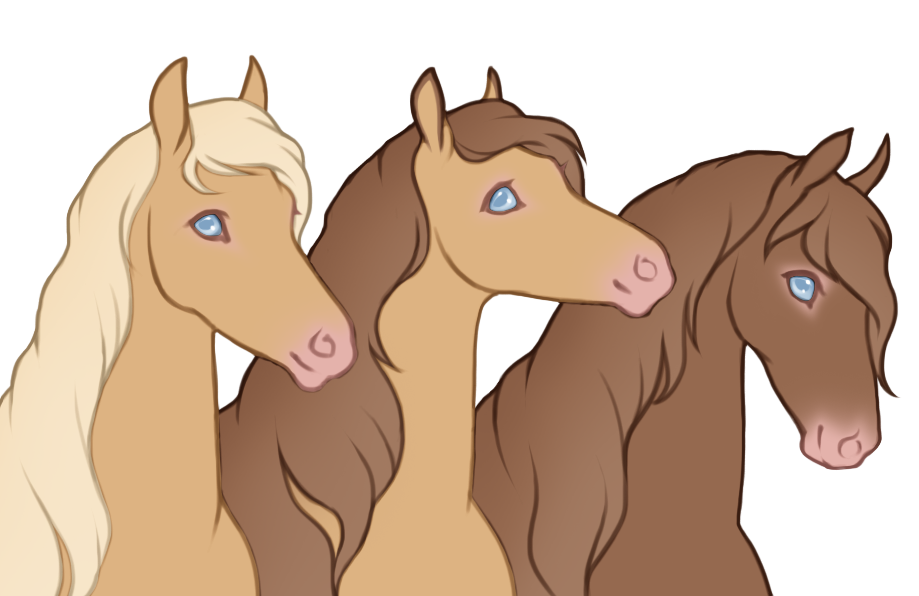
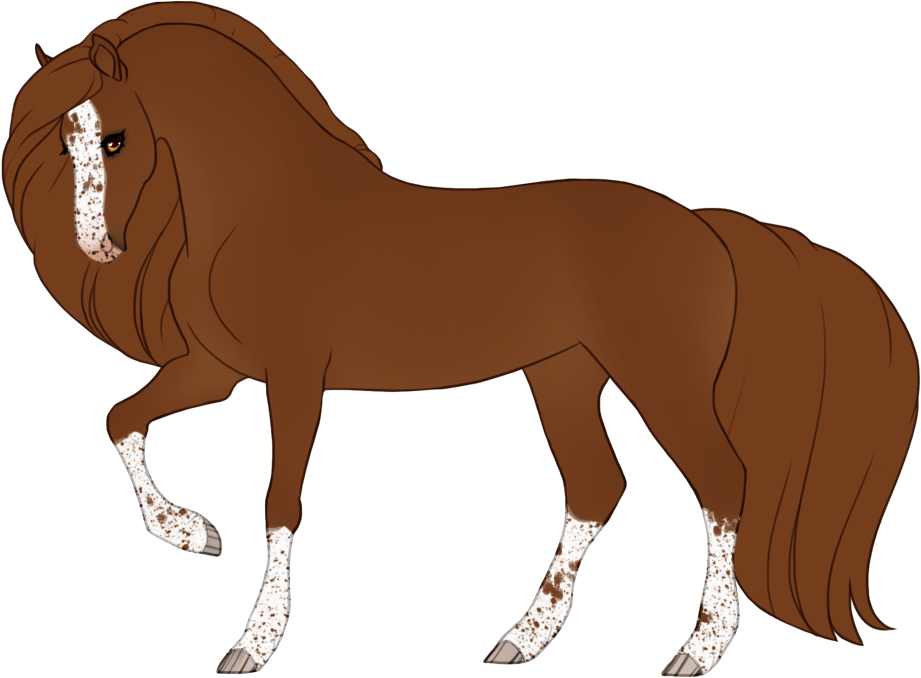
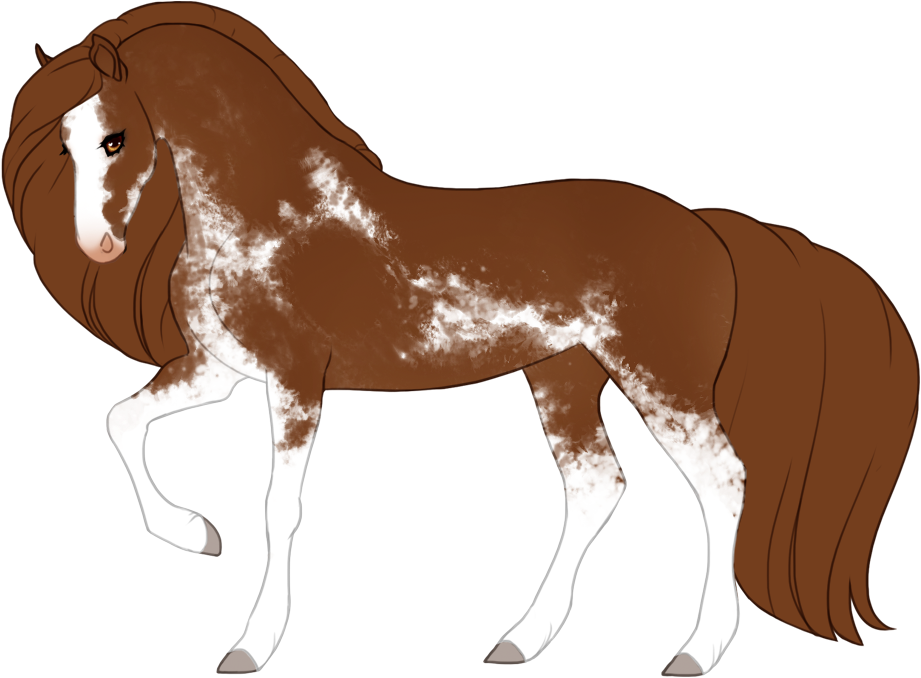
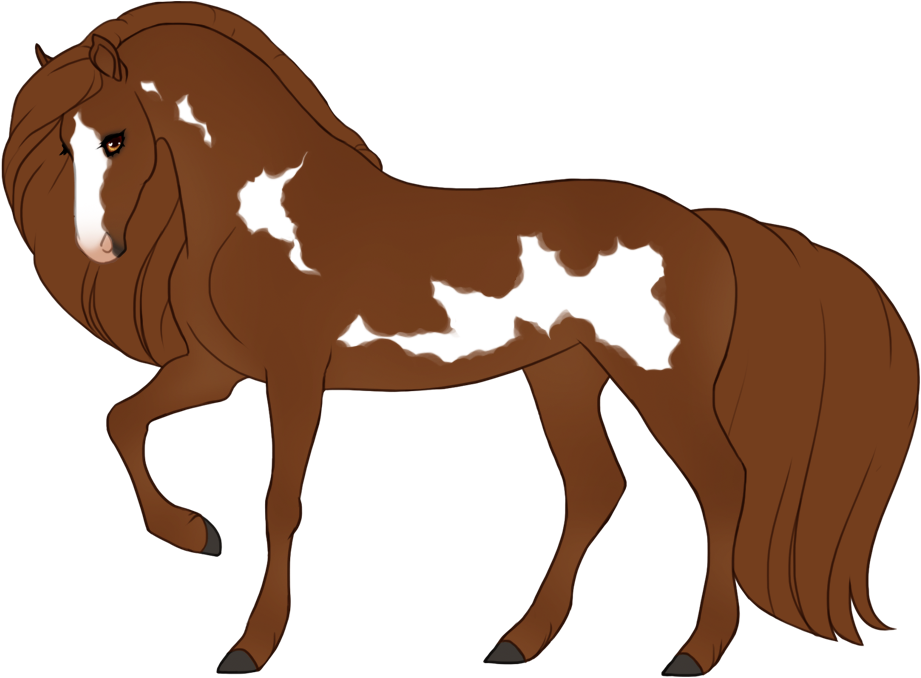
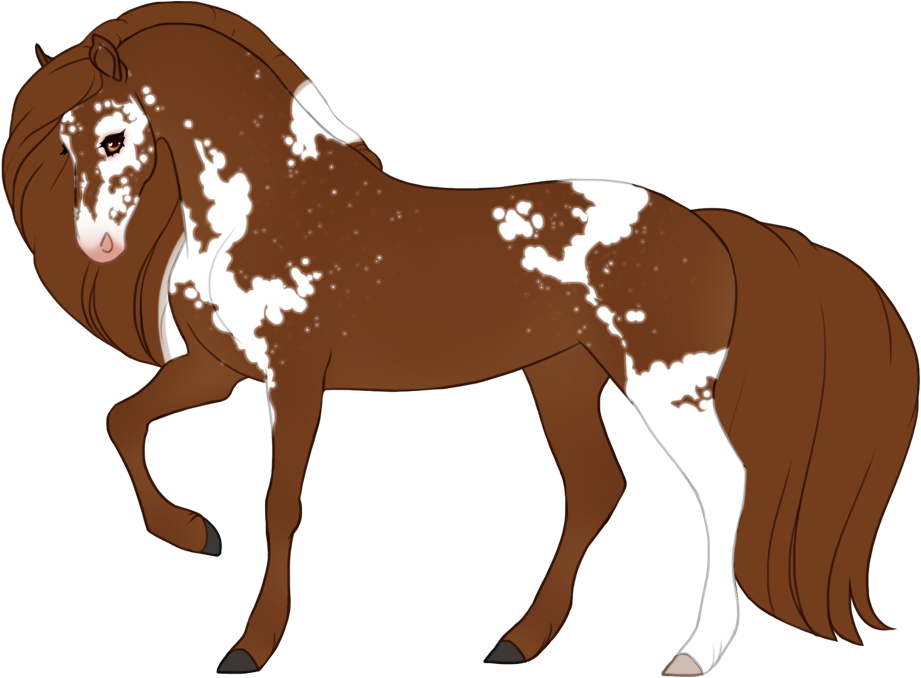
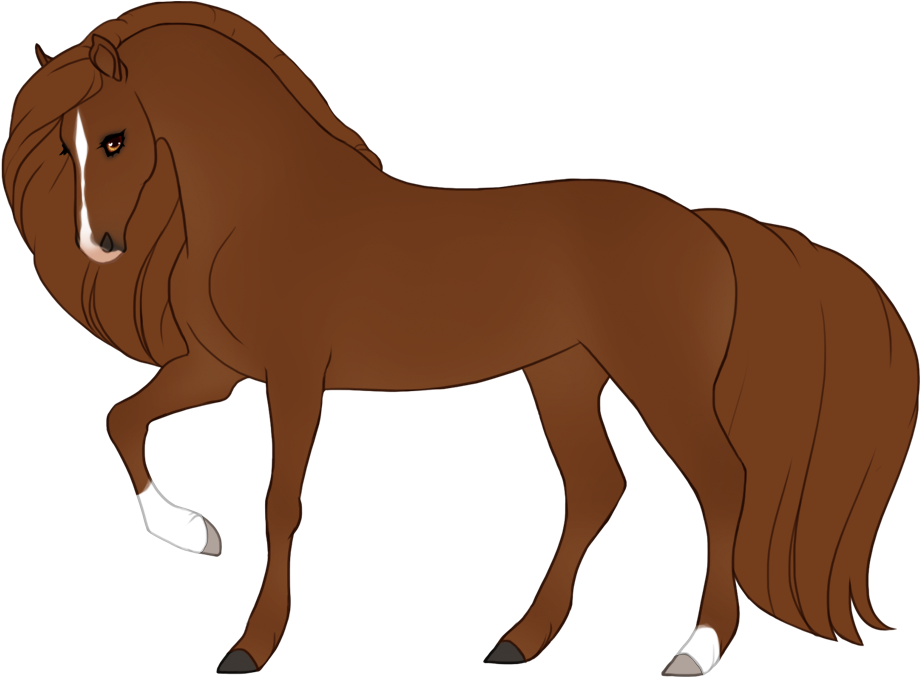
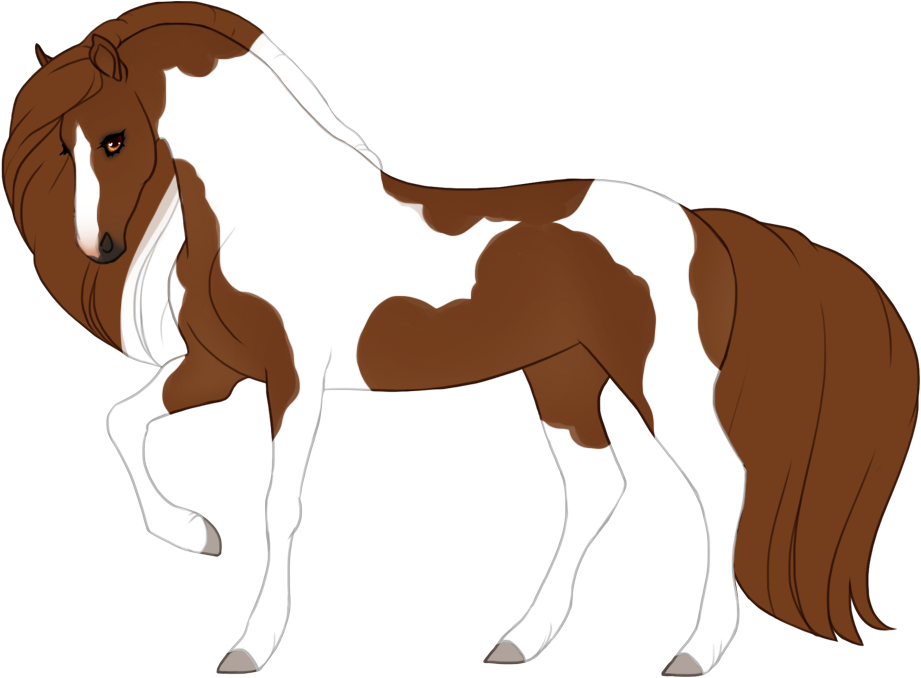
- White patterns cause a lack of color pigment in the coat, resulting in pink skin and white hairs. Skin will always be pink under white markings, the only exception is if the blue dilute is present, then the skin on white markings may be light baby blue (or light purple in the case of tawny+blue).
- Modifiers, Dilutions and Patterns must always go under white patterns, and are also not allowed to "appear" to go over white patterns.
- Can generally cause blue eyes if the white markings reach the eyes, unless otherwise specified.
- Hooves and horns will be lighter when affected by white.
- The minimum expression of each white pattern (except natural white which is optional) can only be reduced with Occlusion, which can partially or fully "turn off" or hide genes.
- Non-heritable traits have a chance to occur on any foal and are rolled at random when the foal genotype is rolled.
- As the name implies, non-heritable traits will not pass to offspring from the horse that has it.